In this post, we will look at how to use Okta to authenticate and authorize requests to an MCP server. We will use the FastMCP library to build both the server and client.
The MCP server we will build will be a wrapper around a simple FastAPI app that’s protected using Okta.
First, we will build a Hello World API using FastAPI and protect its endpoints using Okta. We will create a Okta client for the API and test it with Postman.
Next, we will use FastMCP to convert the API to an MCP server with all its endpoints exposed as tools.
Then we will explore a couple of ways to handle authentication in the MCP server using FastMCP.
TokenVerifier - This just verifies the validity of the token and use the claims in the token for retrieving authorization information to allow access to endpoints
OIDC Proxy - This allows MCP clients to use browser for user authentication and use the token to access the MCP server.
Build the Hello World API with protected endpoints
Let’s use FastAPI to build the Hello World API. This API has 3 endpoints - /health, /hello, and /user. The /health endpoint is open to everyone but /hello and /user are protected by Okta and requires a logged-in user. These protected endpoints rely on the get_current_user() function which verifies the token and extracts the logged in user information from its claims.
The get_current_user() function gets the Bearer token from the Authorization request header, verifies the signature, and decodes it to get the claims present in it.
So, only users authenticated through Okta can access the /hello and /user endpoints.
Make sure to set your OKTA_DOMAIN using an .env file or as an environment variable. The OKTA_ISSUER and JWKS_URI can be obtained from this url - https://<okta-domain.okta.com>/oauth2/default/.well-known/openid-configuration . These can also be obtained from Okta Admin console: Security → API → default (authorization server).
from fastapi import FastAPI, Depends, HTTPException, status
from fastapi.security import HTTPBearer, HTTPAuthorizationCredentials
import jwt
from jwt import PyJWKClient
import os
from typing import Dict, Any
from functools import lru_cache
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import uvicorn
<div></div>
load_dotenv()
<div></div>
# Initialize FastAPI app
app = FastAPI(title="Hello World API", version="1.0.0")
<div></div>
# Security scheme
security = HTTPBearer()
<div></div>
# Configuration
OKTA_DOMAIN = os.getenv("OKTA_DOMAIN", "your-okta-domain.okta.com")
OKTA_AUDIENCE = os.getenv("OKTA_AUDIENCE", "api://default")
OKTA_ISSUER = f"https://{OKTA_DOMAIN}/oauth2/default"
OKTA_JWKS_URI = f"{OKTA_ISSUER}/v1/keys"
<div></div>
# Cached JWK Client
@lru_cache()
def get_jwks_client() -> PyJWKClient:
try:
client = PyJWKClient(OKTA_JWKS_URI)
return client
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error creating PyJWKClient: {e}")
raise
<div></div>
# Simple user model
class User:
def __init__(self, token_claims: Dict[str, Any]):
self.id = token_claims.get("sub")
self.email = token_claims.get("email", token_claims.get("sub"))
self.name = token_claims.get("name", token_claims.get("sub"))
<div></div>
async def get_current_user(credentials: HTTPAuthorizationCredentials = Depends(security)) -> User:
"""Validate Okta bearer token and return user"""
try:
token = credentials.credentials
jwks_client = get_jwks_client()
<div></div>
# Get signing key and verify token
signing_key = jwks_client.get_signing_key_from_jwt(token)
<div></div>
# Decode and verify JWT
decoded_token = jwt.decode(
token,
signing_key.key,
algorithms=["RS256"],
audience=OKTA_AUDIENCE,
issuer=OKTA_ISSUER
)
print(f"Decode Token: {decoded_token}")
return User(decoded_token)
except jwt.ExpiredSignatureError:
print("jwt.ExpiredSignatureError")
raise HTTPException(status_code=status.HTTP_401_UNAUTHORIZED, detail="Token expired")
except jwt.InvalidTokenError:
print("jwt.InvalidTokenError")
raise HTTPException(status_code=status.HTTP_401_UNAUTHORIZED, detail="Invalid token")
except Exception:
print("Exception")
raise HTTPException(status_code=status.HTTP_401_UNAUTHORIZED, detail="Authentication failed")
<div></div>
# Endpoints
@app.get("/health")
async def health_check():
return {"status": "healthy"}
<div></div>
@app.get("/hello")
async def hello_world(user: User = Depends(get_current_user)):
print(f"User:\n{user}")
return {"message": f"Hello, {user.name or user.email}!", "user_id": user.id}
<div></div>
@app.get("/user")
async def get_user_info(user: User = Depends(get_current_user)):
return {
"user_id": user.id,
"email": user.email,
"name": user.name,
"scopes": user.scopes
}
<div></div>
if __name__ == "__main__":
uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=8000)
from fastapi import FastAPI, Depends, HTTPException, status
from fastapi.security import HTTPBearer, HTTPAuthorizationCredentials
import jwt
from jwt import PyJWKClient
import os
from typing import Dict, Any
from functools import lru_cache
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import uvicorn
load_dotenv()
# Initialize FastAPI app
app = FastAPI(title="Hello World API", version="1.0.0")
# Security scheme
security = HTTPBearer()
# Configuration
OKTA_DOMAIN = os.getenv("OKTA_DOMAIN", "your-okta-domain.okta.com")
OKTA_AUDIENCE = os.getenv("OKTA_AUDIENCE", "api://default")
OKTA_ISSUER = f"https://{OKTA_DOMAIN}/oauth2/default"
OKTA_JWKS_URI = f"{OKTA_ISSUER}/v1/keys"
# Cached JWK Client
@lru_cache()
def get_jwks_client() -> PyJWKClient:
try:
client = PyJWKClient(OKTA_JWKS_URI)
return client
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error creating PyJWKClient: {e}")
raise
# Simple user model
class User:
def __init__(self, token_claims: Dict[str, Any]):
self.id = token_claims.get("sub")
self.email = token_claims.get("email", token_claims.get("sub"))
self.name = token_claims.get("name", token_claims.get("sub"))
async def get_current_user(credentials: HTTPAuthorizationCredentials = Depends(security)) -> User:
"""Validate Okta bearer token and return user"""
try:
token = credentials.credentials
jwks_client = get_jwks_client()
# Get signing key and verify token
signing_key = jwks_client.get_signing_key_from_jwt(token)
# Decode and verify JWT
decoded_token = jwt.decode(
token,
signing_key.key,
algorithms=["RS256"],
audience=OKTA_AUDIENCE,
issuer=OKTA_ISSUER
)
print(f"Decode Token: {decoded_token}")
return User(decoded_token)
except jwt.ExpiredSignatureError:
print("jwt.ExpiredSignatureError")
raise HTTPException(status_code=status.HTTP_401_UNAUTHORIZED, detail="Token expired")
except jwt.InvalidTokenError:
print("jwt.InvalidTokenError")
raise HTTPException(status_code=status.HTTP_401_UNAUTHORIZED, detail="Invalid token")
except Exception:
print("Exception")
raise HTTPException(status_code=status.HTTP_401_UNAUTHORIZED, detail="Authentication failed")
# Endpoints
@app.get("/health")
async def health_check():
return {"status": "healthy"}
@app.get("/hello")
async def hello_world(user: User = Depends(get_current_user)):
print(f"User:\n{user}")
return {"message": f"Hello, {user.name or user.email}!", "user_id": user.id}
@app.get("/user")
async def get_user_info(user: User = Depends(get_current_user)):
return {
"user_id": user.id,
"email": user.email,
"name": user.name,
"scopes": user.scopes
}
if __name__ == "__main__":
uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=8000)
Create a client in Okta for the API
Now let’s create an OIDC client in Okta so users can log in and authenticate when invoking the API.
Follow the below steps -
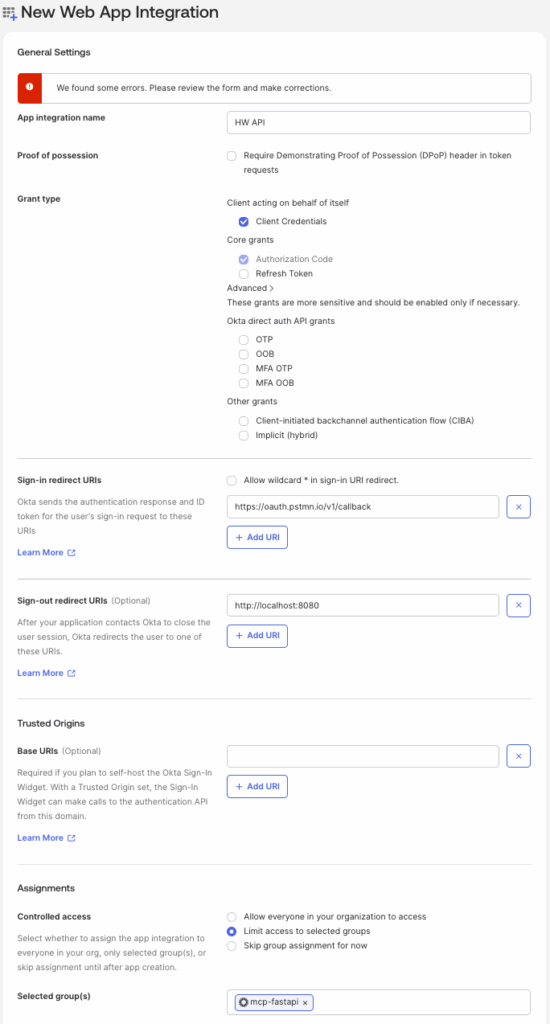
Navigate to Okta Admin console → Applications and click
Create App Integration.Select
OIDC - OpenID Connectoption forSign-in method.Select
Web ApplicationforApplication type.Provide a name for
App Integration name, for example -HW API.Select
Client CredentialsinGrant type.Provide the Postman Callback URL
https://oauth.pstmn.io/v1/callbackin theSign-in redirect URIsas we will use Postman to test the API.If you already have a group with users assigned in Okta, select
Limit access to selected groupsunder Assignments → Controlled Access. Otherwise, just selectAllow everyone in your organization to access.Click
Save.
Test the API with Postman
Let’s test our API in Postman. Create a new request for the endpoint http://localhost:8000/hello
and configure the Authorization tab as follows.
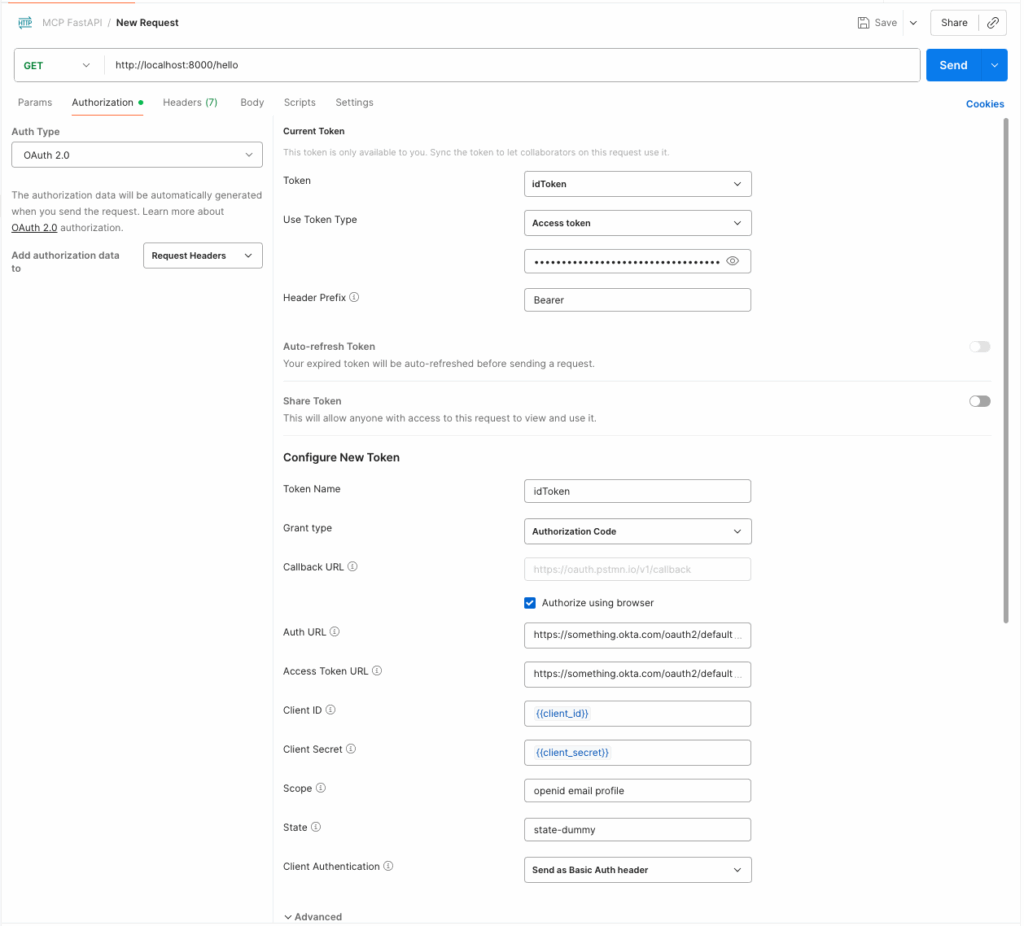
Select
OAuth 2.0forAuth type.In the
Configure New Tokensection -Enter
Token NameasidTokenSelect
Grant typeasAuthorization CodeSelect
Authorize using browserSelect
Auth URLas https://<your-okta-domain.okta.com>/oauth2/default/v1/authorizeSelect
Access Token URLas https://<your-okta-domain.okta.com>/oauth2/default/v1/tokenGet the
client idandclient secretfor the new app that we created in Okta and provide it as the value forClient IDandClient Secret.Provide
openid email profileas the value forScope.Provide some dummy value for
Statesuch asstate-dummy.Select
Client AuthenticationasSend as Basic Auth header.Note: After you authenticate and get a token, go to the
Current Tokensection, selectidTokenfrom theAvailable Tokensand chooseAccess TokenforUse Token Typeoption. We will use thatAccess Tokenas the Bearer token when calling the API.
Finally, test the API by clicking Get New Access Token and logging into Okta.
Create a MCP Server for Hello World API
Now that our Hello World API works with Okta authentication, let’s use FastMCP to create an MCP server from this API and apply the same user authentication with Okta.
There are a few ways to set up authentication for an MCP Server and we will look at two of them below. Please refer to FastMCP docs for more reading on the various authentication methods.
Method 1: Token Verifier authentication
This is the simplest approach - the MCP Server just verifies the incoming authorization token and doesn’t handle user login workflow. The MCP client will have to provide the authorization token in the header while invoking the server.
Here’s the implementation of the MCP Server for our Hello World API. We configure the token issuer, signing keys and audience so FastMCP can validate tokens and either grant access or return a 401 error.
# MCP Server for Hello World API
<div></div>
from fastmcp import FastMCP
from hw_api_with_auth import app
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
<div></div>
load_dotenv()
<div></div>
# Convert to MCP server
mcp = FastMCP.from_fastapi(app=app)
<div></div>
if __name__ == "__main__":
mcp.run(transport='sse')
# MCP Server for Hello World API
from fastmcp import FastMCP
from hw_api_with_auth import app
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
load_dotenv()
# Convert to MCP server
mcp = FastMCP.from_fastapi(app=app)
if __name__ == "__main__":
mcp.run(transport='sse')
#.env file for MCP Server
FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH=fastmcp.server.auth.providers.jwt.JWTVerifier
<div></div>
FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH_JWT_JWKS_URI="https://<your-okta-domain.okta.com>/oauth2/default/v1/keys"
FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH_JWT_ISSUER="https://<your-okta-domain.okta.com>/oauth2/default"
FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH_JWT_AUDIENCE="api://default"
FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH_JWT_REQUIRED_SCOPES="email"
#.env file for MCP Server
FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH=fastmcp.server.auth.providers.jwt.JWTVerifier
FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH_JWT_JWKS_URI="https://<your-okta-domain.okta.com>/oauth2/default/v1/keys"
FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH_JWT_ISSUER="https://<your-okta-domain.okta.com>/oauth2/default"
FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH_JWT_AUDIENCE="api://default"
FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH_JWT_REQUIRED_SCOPES="email"
Test the MCP Server with MCP Inspector
Start the MCP Server
uv run hello_world_mcp_server.py
uv run hello_world_mcp_server.py
Start MCP Inspector
npx @modelcontextprotocol/inspector
npx @modelcontextprotocol/inspector
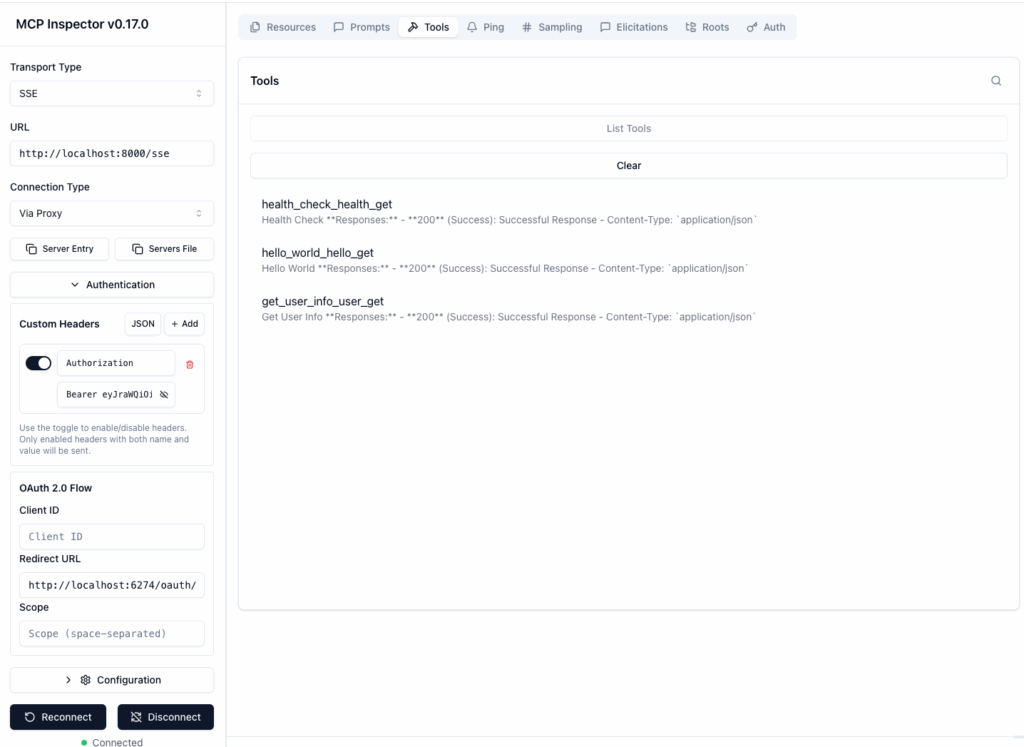
Configure Inspector as below
Select
Transport TypeasSSEEnter the
URLof your MCP server -http://localhost:8000/sseOpen the
Authenticationtab, enable theAuthorizationheader and enterBearer <your access token from okta login>Click
ConnectClick
Toolson the tab above in the right. It should display the three API endpoints as tools.Select either the
hello_world_hello_getorget_user_info_user_gettools to test the MCP server with authentication.
Test the MCP Server with a custom MCP client
import asyncio
from fastmcp import Client
<div></div>
async def main():
<div></div>
async with Client(
"http://localhost:8000/sse",
auth="<your-access-token>"
) as client:
await client.ping()
<div></div>
result = await client.call_tool("health_check_health_get")
print(f"Health Check Result: {result}")
<div></div>
result = await client.call_tool("hello_world_hello_get")
print(f"Hello World GET Result: {result}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
import asyncio
from fastmcp import Client
async def main():
async with Client(
"http://localhost:8000/sse",
auth="<your-access-token>"
) as client:
await client.ping()
result = await client.call_tool("health_check_health_get")
print(f"Health Check Result: {result}")
result = await client.call_tool("hello_world_hello_get")
print(f"Hello World GET Result: {result}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
Method 2: OIDC Proxy
We can use OIDC Proxy approach by configuring a pre-registered Okta client directly in the MCP Server. The OIDC Proxy allows us to use the pre-registered client bypassing the Dynamic Client Registration expected by MCP Server.
Below you can see the MCP Server and client using OIDC proxy. This approach opens a browser window for user login and automatically sends the resulting access token with each request in the authorization header.
Build the MCP Server
# MCP Server using OIDC Proxy
from fastmcp import FastMCP
from fastmcp.server.auth.oidc_proxy import OIDCProxy
from hw_api_with_auth import app
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
<div></div>
load_dotenv(".env_hw_api_mcp_server_oidc_proxy")
<div></div>
CONFIG_URL = os.getenv("FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH_CONFIG_URL")
CLIENT_ID = os.getenv("FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH_CLIENT_ID")
CLIENT_SECRET = os.getenv("FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH_CLIENT_SECRET")
AUTH_AUDIENCE = os.getenv("FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH_AUDIENCE")
AUTH_BASE_URL = os.getenv("FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH_BASE_URL")
<div></div>
# Create the OIDC proxy
auth = OIDCProxy(
# Provider's configuration URL
config_url=CONFIG_URL,
<div></div>
# Your registered app credentials
client_id=CLIENT_ID,
client_secret=CLIENT_SECRET,
<div></div>
# Your FastMCP server's public URL
base_url=AUTH_BASE_URL
)
<div></div>
# Convert the API to MCP server
mcp = FastMCP.from_fastapi(app=app, auth=auth)
<div></div>
if __name__ == "__main__":
mcp.run(transport='sse')
# MCP Server using OIDC Proxy
from fastmcp import FastMCP
from fastmcp.server.auth.oidc_proxy import OIDCProxy
from hw_api_with_auth import app
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
load_dotenv(".env_hw_api_mcp_server_oidc_proxy")
CONFIG_URL = os.getenv("FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH_CONFIG_URL")
CLIENT_ID = os.getenv("FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH_CLIENT_ID")
CLIENT_SECRET = os.getenv("FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH_CLIENT_SECRET")
AUTH_AUDIENCE = os.getenv("FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH_AUDIENCE")
AUTH_BASE_URL = os.getenv("FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH_BASE_URL")
# Create the OIDC proxy
auth = OIDCProxy(
# Provider's configuration URL
config_url=CONFIG_URL,
# Your registered app credentials
client_id=CLIENT_ID,
client_secret=CLIENT_SECRET,
# Your FastMCP server's public URL
base_url=AUTH_BASE_URL
)
# Convert the API to MCP server
mcp = FastMCP.from_fastapi(app=app, auth=auth)
if __name__ == "__main__":
mcp.run(transport='sse')
#.env file for MCP Server
FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH_CONFIG_URL=https://<your-okta-domain.okta.com>/oauth2/default/.well-known/openid-configuration
FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH_CLIENT_ID=<client_id>
FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH_CLIENT_SECRET=<client_secret>
FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH_AUDIENCE="api://default"
FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH_BASE_URL=http://localhost:8000
#.env file for MCP Server
FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH_CONFIG_URL=https://<your-okta-domain.okta.com>/oauth2/default/.well-known/openid-configuration
FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH_CLIENT_ID=<client_id>
FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH_CLIENT_SECRET=<client_secret>
FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH_AUDIENCE="api://default"
FASTMCP_SERVER_AUTH_BASE_URL=http://localhost:8000
Build the MCP Client
The MCP Client below triggers the OAuth flow - if no valid token is found, it opens your browser so you can provide the credentials and login to Okta. For more details, refer to this FastMCP documentation .
# MCP Client
import asyncio
from fastmcp import Client
from fastmcp.client.auth import OAuth
<div></div>
async def main():
oauth = OAuth(mcp_url="https://<your-okta-domain.okta.com>/oauth2/default")
<div></div>
async with Client("http://localhost:8000/sse", auth=oauth) as client:
# Automatic browser-based OAuth flow
await client.ping()
<div></div>
result = await client.call_tool("health_check_health_get")
print(f"Health Check Result: {result}")
<div></div>
result = await client.call_tool("hello_world_hello_get")
print(f"Hello World GET Result: {result}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
# MCP Client
import asyncio
from fastmcp import Client
from fastmcp.client.auth import OAuth
async def main():
oauth = OAuth(mcp_url="https://<your-okta-domain.okta.com>/oauth2/default")
async with Client("http://localhost:8000/sse", auth=oauth) as client:
# Automatic browser-based OAuth flow
await client.ping()
result = await client.call_tool("health_check_health_get")
print(f"Health Check Result: {result}")
result = await client.call_tool("hello_world_hello_get")
print(f"Hello World GET Result: {result}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
Test the MCP Server with custom MCP Client
Start the MCP server
uv run mcp_server.py
uv run mcp_server.py
Start the MCP client
uv run mcp_client.py
uv run mcp_client.py
If everything works, you will see output like below in your logs for the tool calls.
Health Check Result: CallToolResult(content=[TextContent(type='text', text='{"status":"healthy"}', annotations=None, meta=None)], structured_content={'status': 'healthy'}, data={'status': 'healthy'}, is_error=False)
Hello World GET Result: CallToolResult(content=[TextContent(type='text', text='{"message":"Hello, Selvam Subbiah!","user_id":"selvam.subbiah@something.com"}', annotations=None, meta=None)], structured_content={'message': 'Hello, Selvam Subbiah!', 'user_id': 'selvam.subbiah@something.com'}, data={'message': 'Hello, Selvam Subbiah!', 'user_id': 'selvam.subbiah@something.com'}, is_error=False)
Health Check Result: CallToolResult(content=[TextContent(type='text', text='{"status":"healthy"}', annotations=None, meta=None)], structured_content={'status': 'healthy'}, data={'status': 'healthy'}, is_error=False)
Hello World GET Result: CallToolResult(content=[TextContent(type='text', text='{"message":"Hello, Selvam Subbiah!","user_id":"selvam.subbiah@something.com"}', annotations=None, meta=None)], structured_content={'message': 'Hello, Selvam Subbiah!', 'user_id': 'selvam.subbiah@something.com'}, data={'message': 'Hello, Selvam Subbiah!', 'user_id': 'selvam.subbiah@something.com'}, is_error=False)
